Often, we wonder, how can a simple click on a checkbox prove that I am a human. Aren’t computer bots smart enough nowadays to simply fool a checkbox to prove their humanness? How does the website verify the humanness of a simple click? Although these questions are simple enough, the answer is not as much. Let’s understand together what happens under the hood of just a simple mouse click. 🐭
The CAPTCHA Metamorphosis: From Words to Clicks ⏳
Developed in the early 2000s, CAPTCHA or “Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart” is used to differentiate between a robot and a human. Developers have built Captchas with text to no verification throughout the years, keeping in mind how it will secure the websites as well as make it easier for the users to prove they’re human.
Text-based CAPTCHAs 💬
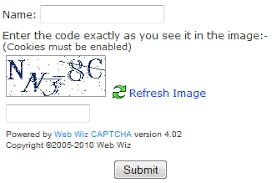
It involved users inputting distorted sequences of characters in a form field to prevent the form submitted by any bot millions of times. These were widely used for several years but research showed that humans were wasting an average of 500,000 hours per day completing these CAPTCHAs. This gave birth to a powerful and meaningful tool to make use of this time – reCAPTCHAs.
reCAPTCHA 🪃

Luis von Ahn, a member of the original research team for CAPTCHAs, wanted to make use of this valuable time. Projects and companies such as Amazon Kindle, Google Books, The New York Times and more, were heavily involved in scanning and indexing large amounts of books, documents and images for the web. But the problem is, that most of the texts, which are aged, are not interpreted accurately by OCR.
reCAPTCHA solves this problem by displaying scanned words that cannot be recognized by machines, along with a known word, to a human user. If the user correctly types the known word, it verifies them as human and increases the system's confidence that the unrecognized word has been accurately transcribed.
Google acquired reCAPTCHA in 2009 to support its ambitious project, Google Books, which aimed to digitize every book in the world and create a vast digital library accessible to everyone. However, the project faced some setbacks and did not achieve its original goals. Despite this, reCAPTCHA continues to be widely used today as an effective tool to prevent automated access and improve online security.
I have come across an interesting video, take a look at this TED talk!
No CAPTCHA reCAPTCHA 💡
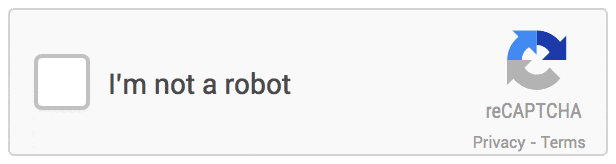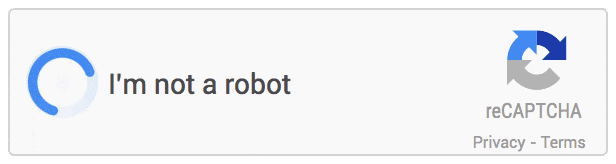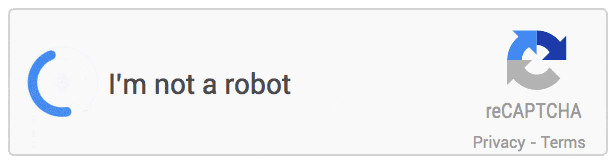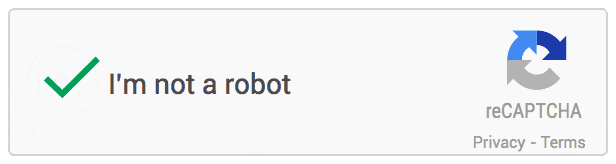
The checkbox that we see nowadays which just requires a simple click is called “No CAPTCHA reCAPTCHA”. When a user clicks on the checkbox, a request is sent to Google with details of your browsing history, activity in Gmail, how many YouTube videos you’ve watched, screen size & resolution, IP address, random mouse clicks, taps, scrolls, browser cookies and many more. It makes use of an Advanced Risk Analysis Engine to analyze this information and to make a conclusion about your humanness. Post the analysis, Google returns a score to the website and if the score is high, the user is allowed into the website.
There might be cases when the analysis is inconclusive. In such events, you will fall back to the reCAPTCHA method of verification as an additional security measure.
NOTE - The digital footprints of a user is difficult to imitate by scripts and bots due to the randomness of human behaviour and acts as the most distinguishing factor between human and robot. By clicking on the checkbox, we are permitting Google to access all the data needed for verifying us as humans 👀.
Beyond Text-Based Challenges: Common Alternatives in CAPTCHAs 🎧
Image Recognition CAPTCHA 📸

It is a type of CAPTCHA, based on a classic Computer Vision problem of image labelling, that requires the user to select specific images from a set that meets certain criteria while excluding others that do not. It is used particularly in mobile devices. Image Recognition CAPTCHAs are more resistant to automated attacks, as they require more advanced image recognition algorithms to solve.
Audio Recognition CAPTCHA 🔊
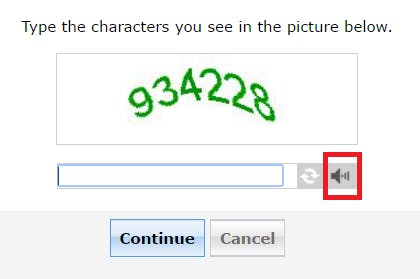
It is a type of CAPTCHA that requires the user to listen to a series of audio clips and transcribe them into text. The audio clips typically contain a spoken word or phrase that is distorted or spoken with background noise to make it difficult for automated systems to decipher. The user is then asked to type in what they hear to confirm their human identity.
Math Problem CAPTCHA 📑

It is a type of CAPTCHA that presents the user with a simple math problem, such as addition or subtraction, that they must solve to prove their identity as a human. They may not be suitable for all websites or applications, as they may not provide enough security for more sensitive data or transactions.
Why They're Critical for Your Online Security 👾
CAPTCHA offers us security from various online threats. Malicious bots or software applications tend to annoy users by spreading spam content, taking control over accounts or bringing down websites by executing DDOS attacks. These may result in damaging the integrity of the overall website, inaccessibility of resources to valid users or breaking into accounts by brute-force attacks. Such attacks can directly or indirectly affect millions of people globally, including huge monetary losses. That is why CAPTCHAs are critical for implementing security measures and allowing users a safe environment to view genuine resources.
Conclusion 🤘🏼
CAPTCHAs may seem like a small box with a simple task, but behind the scenes, they're the guardians of the internet, keeping bots and spam at bay. So next time you're asked to prove you're not a robot, give a virtual high-five to these unsung heroes, for protecting our online world one click at a time! 🫱🏻🫲🏽

